Introduction to Diabetic Watches
In the realm of health technology, diabetic watches mark a significant innovation. These devices offer an advanced way for individuals with diabetes to keep track of their blood sugar levels effortlessly.

Unlike traditional methods that often require finger pricks and blood samples, diabetic watches strive to simplify glucose monitoring. They bridge the gap between continuous health tracking and everyday convenience, making them an essential tool for diabetes management.
At their core, diabetic watches work by integrating with sensors that measure glucose levels either through the skin or via interstitial fluids. They then display this information directly on the watch face or relay it to an associated smartphone app for deeper analysis and historical data tracking.
With the evolving technology, the compatibility and features of these diabetic watches continue to improve. This offers greater control and peace of mind for users who can now monitor their health metrics in real-time, right from their wrists.
This introduction to diabetic watches will lead us through their transformative journey – from their origins to cutting-edge non-invasive monitoring solutions. Following through, we’ll explore the critical features, brand comparisons, integration with mobile devices, and the significant role of FDA approvals in ensuring their safety and reliability.
Evolution of Glucose Monitoring Technology
The journey of glucose monitoring has been remarkable. What began with finger-pricking devices has evolved into sophisticated technology. Early monitors required blood samples. They were often painful and inconvenient for daily use.
Now, we witness a revolution in how these levels are tracked. Modern diabetic watches operate with advanced sensors. These sensors detect glucose through skin contact or interstitial fluids. No need for blood makes it less daunting for users.
The adoption of non-invasive methods has skyrocketed interest. Companies focus on creating watches that offer pain-free monitoring. This has led to innovative products in the diabetic care market.
In recent years, smartwatch integration has become a game-changer. Diabetic watches now sync with mobile apps for analysis. They offer real-time data and keep a history of glucose levels. This aids better diabetes management.
The constant push for progress has brought us to potential noninvasive diabetic watches. Although still in development, this technology could represent a breakthrough. It aims to monitor glucose without any skin breach at all.
In conclusion, glucose monitoring technology is at a pivotal point. From manual blood samples to potential noninvasive smart devices, the future looks promising. These advances may soon bring even more comfort and control to individuals with diabetes.
 Features of Current Diabetic Smartwatches
Features of Current Diabetic Smartwatches
Today’s diabetic smartwatches are marvels of technology. They come packed with features that make daily diabetes management more manageable and less intrusive. Key features you’ll find in most of these innovative devices include:
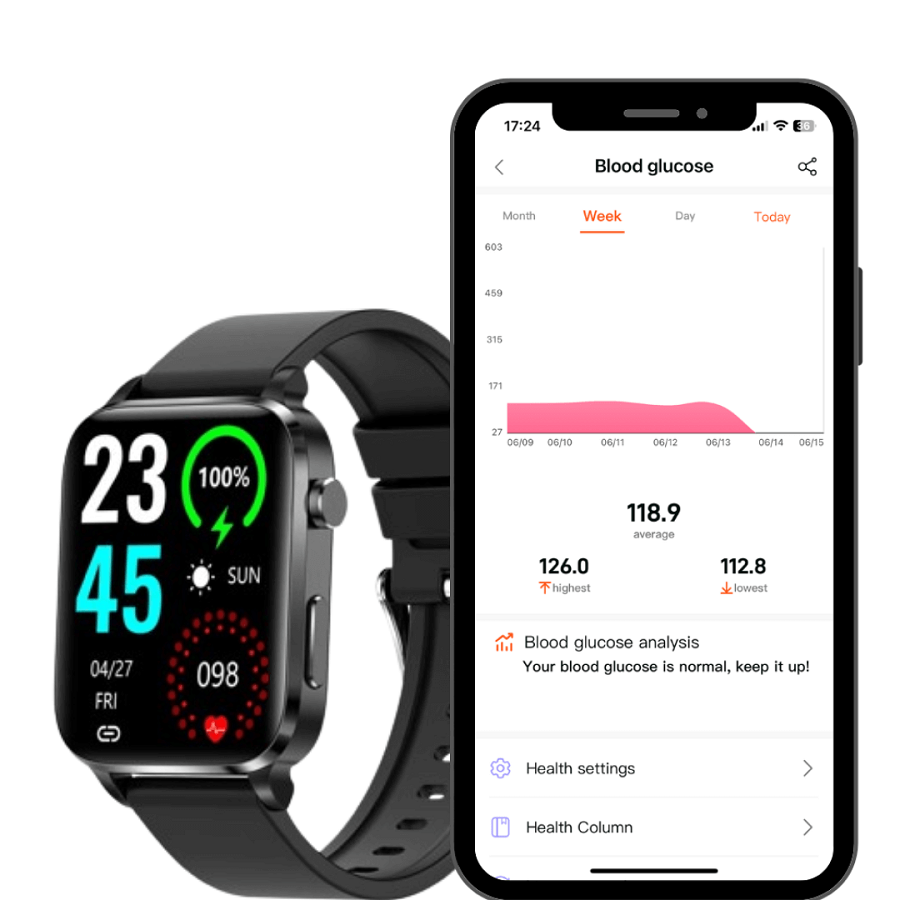
- Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring: The highlight of these watches is their ability to check glucose levels without skin punctures. Sensors read through the skin or interstitial fluids.
- Real-Time Alerts: Users receive instant notifications for high or low blood sugar levels. This timely information can be lifesaving.
- Data Syncing with Apps: Glucose data syncs with mobile apps. This allows for in-depth analysis and easy tracking over time.
- Customizable Displays: Users can choose how to view their data. Watch faces often show current glucose levels and trends.
- Activity Tracking: These watches also function as fitness trackers. They monitor steps, heart rate, and sometimes sleep patterns.
-Low Power Usage and Wireless Charging: Keeps the device running longer.
- Remote Sharing Capabilities: Some models let users share data with doctors or family members. This ensures better support and monitoring.
- Water Resistance: Many watches are water-resistant. This allows users to wear them during various activities without worry.
These features not only support diabetes management but also contribute to overall health monitoring. As technology advances, we expect even more user-centered features to emerge, enhancing the quality of life for those with diabetes.
 Comparing Diabetic Smartwatch Brands and Models
Comparing Diabetic Smartwatch Brands and Models
Choosing the right diabetic watch involves comparing various brands and models. Here’s a quick overview:
Dexcom Watches:
Pioneers in displaying glucose data on smartwatches. Compatible with multiple smartwatch models and offer a range of display options. Dexcom continues to innovate with the promise of direct smartwatch connectivity in newer models like the G7.
Garmin Watches:
Known for sports and fitness tracking, they’ve entered the diabetic watch market showing real-time CGM data directly on the watch face. They are FDA approved for safety and accuracy in diabetes care.
Medtronic Devices:
Focus mainly on insulin pumps with integrated CGM systems, like the Medtronic 770G. They offer stand-alone CGM solutions that send notifications to smartwatches.
Eversense CGM:
Provides an implantable CGM option, which pairs with smartphones. Although completely dependent on a smartphone app, it offers compatibility with Apple Watch and is exploring Android smartwatch connectivity.
FreeStyle Libre Systems:
Abbott’s Flash Glucose Monitors are popular for not needing finger-pricks. They rely on scanning sensors but have DIY solutions for smartwatch connectivity.
Fitbit Watches:
Started with Pebble watch technology for the integration of CGM data through third-party apps and now offers native solutions with some of their newer models.
Each brand and model has unique features, like real-time CGM data, fitness tracking, and even smart connectivity features. The differences mainly lie in their approach to glucose monitoring, third-party app availability, and the kind of data they offer to the users.
When comparing diabetic smartwatches, consider ease of use, real-time alerts, data syncing capabilities, and battery life. Also, remember to consider whether the device integrates well with other health devices and the extent to which it fits into daily life seamlessly.
In summary, the best diabetic smartwatch for an individual will depend on their specific needs and lifestyle preferences. It’s important to keep these considerations in mind when browsing the market.
How Diabetic Watches Integrate with Mobile Devices
The integration of diabetic watches with mobile devices is a leap forward in managing diabetes. This pairing offers several benefits, enhancing both convenience and the efficacy of monitoring.
- Data Sharing and Management: Diabetic watches sync data with mobile apps. This lets users view detailed analyses and track blood sugar trends over time.
- Customized Alerts: Users receive notifications on their smartphones. These can signal high or low blood sugar, prompting quick action.
- Remote Monitoring: Family and healthcare providers can check glucose levels. This happens through shared data from the watch’s app, offering a support system for the user.
- Software Updates: Mobile connectivity allows for easy updates to the watch’s software. This ensures you always have the latest features and improvements.
- Compatibility: Many watches work with both iOS and Android. This wide range caters to most smartphone users.
- Ease of Use: Setting up and syncing is made simple. Users can do this with minimal effort, owing to user-friendly app interfaces.
- Accessibility: With mobile integration, data is at your fingertips. This improves accessibility for users to manage their health on the go.
Mobile integration is key to the modern diabetic watch experience. It simplifies diabetes management by keeping users connected and informed at all times.
 The Role of FDA in Diabetic Watch Approvals
The Role of FDA in Diabetic Watch Approvals
The FDA’s role is crucial in diabetic watch approvals. It provides oversight to ensure these devices are safe and effective for users. Every diabetic watch must undergo strict FDA evaluations before hitting the market. This includes clinical trials and accuracy tests. The FDA checks if the devices correctly monitor glucose levels. They also assess the potential risks and benefits to users. FDA approval means a diabetic watch has met the agency’s high standards.
Here are key points in the FDA’s approval process for diabetic watches:
- Evaluation of Safety: The FDA reviews to confirm the watch does not harm users.
- Accuracy Testing: They rigorously test to ensure glucose readings are consistent and reliable.
- Clinical Trials: Watches go through trials to demonstrate their effectiveness in real-world settings.
- Compliance Checks: The FDA ensures watches meet all regulatory requirements.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Even after approval, the FDA monitors watches for any issues that arise.
Manufacturers must report to the FDA on watch performance. They outline how they deal with any problems. Users can also submit reports on issues they encounter. These safeguards help maintain the trust and reliability of diabetic watches.
The FDA does not approve products lightly. Their endorsement is a significant achievement for any diabetic watch. It indicates a product you can trust for accuracy and safety. This confidence is vital for those relying on diabetic watches for daily diabetes management. The FDA’s stringent approval process plays an essential role in advancing diabetic care technology.
DIY Solutions and Third-Party Apps for Diabetes Management
The diabetes community has witnessed a surge in DIY solutions and third-party apps. These options add flexibility and personalization to diabetes management. Here’s how they are shaping the user experience:
- Customization and Control: DIY projects allow users to tailor their diabetes management tools to fit their specific needs better.
- Innovative Tracking: Several third-party apps enable users to log and analyze their glucose data beyond basic tracking, incorporating diet and exercise information.
- Community Support: Online communities share knowledge and support, which empowers users to create and use DIY solutions.
- Cost-Effective Options: Many of these solutions and apps are less expensive than traditional systems, making diabetes management more accessible to a broader audience.
- Compatibility with Various Devices: They often offer integration with a range of devices, giving users more choice and flexibility in how they monitor their diabetes.
- Continuous Enhancements: Developers regularly update apps and solutions, constantly improving features and usability.
DIY solutions and third-party apps have become vital in diabetes management. They offer customization, innovation, community support, and cost savings. These benefits complement the use of diabetic watches, enhancing the overall strategy for managing diabetes.
 Future Advances and Research in Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
Future Advances and Research in Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
The pursuit of non-invasive glucose monitoring is revolutionizing diabetes care. Researchers tirelessly push the boundaries, seeking ways to measure blood sugar without skin penetration. These visionary technologies are not far from reality and could bring ease and accuracy to diabetes management.
Ongoing research focuses on various methods. Light-based sensors and bio-fluid analysis stand out among them. Work on devices that read glucose levels from tears, sweat, or interstitial fluids is significant. Moreover, progress with light sensors that detect blood sugar through the skin is promising.
Companies are also striving for innovation. Some are exploring watches that predict hyper or hypoglycemic events without direct glucose measurement. This could be a precursor to fully non-invasive monitoring tools.
Recently, regulatory warnings against unauthorized devices highlight the challenges. The FDA has stressed the importance of accurate, approved technology due to the severe risks of incorrect data.
Indeed, hurdles like FDA approvals make the road to commercial availability a long one. Yet, the promise of a convenient, non-painful way to check glucose motivates researchers and companies alike.
Expectations for the future are grounded. Non-invasive monitors might first serve as early warning systems or fitness aids. Down the line, they could evolve into primary monitoring tools for diabetes management.
For people living with diabetes, these advancements offer hope. A future free from finger pricks is within grasp. The integration of these advanced technologies into everyday life could transform the diabetes care landscape forever.
